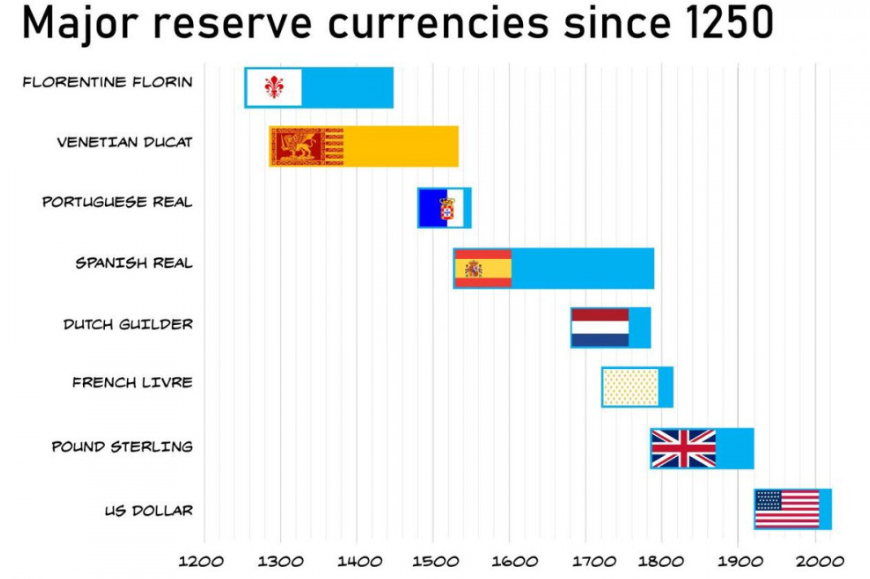
In December last year, we wrote about Javier Milei – the recently elected President of Argentina. Now, with his recent speech in Davos, he has turned the bottom into the top.
To understand what happened and what Milei got himself into, you first need to comprehend what exactly the World Economic Forum (WEF) is and who makes it up. The WEF is the world’s elite: the CEOs of the world’s richest companies (only companies with billions in revenue are invited to the Forum), leading bankers and technology specialists, politicians, representatives of major business organizations, lobbyists, selected intellectuals, journalists and activists of all kinds. The WEF meetings are therefore full of people who use their connections and influence to try to steer the world in a direction that benefits them and not necessarily the majority of people. It’s about power and money, not about a better life for ordinary citizens.
The aforementioned elite meet every year in Davos to present their proposals on how they want to intervene in our lives. They negotiate agreements among themselves and exert pressure on the world’s most influential politicians. In the meantime, of course, there is a lot of empty talk and boring debates about the world’s social and economic problems. The founder of the forum is Klaus The-Great-Reset Schwab, who became known as an advocate of collectivism. He is credited with the famous saying: You will have nothing and be happy.
This is where Milei comes into play. In a place where the ideas of feminism, birth control and increased government intervention in the economy are supported year after year, where the foundations for Agenda 2030 and its associated eco-terrorism were laid, Milei looks the globalists in the eye and dismantles their propaganda simply and vividly by exposing the lies of the globalists.
In many of his interviews and speeches, Milei refers to the so-called culture war. In his view, the causes of Argentina’s decline are cultural problems and moral decay. Among other things, this gives rise to the deep belief that the state is the guarantor for the satisfaction of citizens’ needs. At the same time, the Argentinian president points out that state intervention is counterproductive, as it should only contribute to the opposite when trying to solve a problem.
Here we summarize the most important theses of his speech in Davos:
1. Capitalism creates prosperity and is moral
Socialism leads to impoverishment and is based on violence. Wherever socialism has been introduced, it has brought more harm than good.
“The West is in danger because it has opened itself up to socialist ideas. It was capitalism that liberated humanity from mass poverty and created unimaginable prosperity. (…) In the countries where we should be defending the values of the free market, private property and other institutions of libertarianism, parts of the political and economic establishment – some because of flaws in their theoretical approach, others out of a desire for power – are undermining the foundations of libertarianism by opening the door to socialism and potentially condemning us to poverty, misery and stagnation. It should never be forgotten that socialism is always and everywhere an impoverishing phenomenon that has failed in all countries where it has been tried. It has failed economically as well as socially and culturally. It has also contributed to the deaths of more than 100 million people.”
So capitalism, rather than today’s Western neo-Marxism, is the way to abolish poverty.
2. Socialism is a repressive and unjust system:
“(…) Social justice is neither fair nor beneficial to society. Quite the opposite. It is an inherently unjust idea because it is based on force. It is unjust because the state is financed by taxes and taxes are levied by force. Or would any of you say that you pay taxes of your own free will? In other words, the state finances itself through coercion, and the higher the tax burden, the greater the coercion and the less the freedom. Advocates of social justice assume that the entire economy is a cake that can be shared. Yet, this cake did not fall from the sky. It is wealth created by what Israel Kirzner, for example, calls the process of market discovery. If there is no demand for the goods produced by a company, that company will fail if it does not adapt to the demands of the market. If it produces a good quality product at an attractive price, then it will be successful and produce more because the market is a process of discovery in which the capitalist finds the right direction in the course of his actions. If the state, however, punishes the capitalist for his success and blocks him in this discovery process (through excessive regulation, as in the EU – author’s note), it destroys his motivation, and the result is that he produces less and the pie shrinks, which damages society as a whole. By inhibiting these processes of discovery and making it difficult to adopt what has been discovered, collectivism inhibits the entrepreneur and prevents him from flourishing.”
3. The fight for women’s rights or nature conservation is just a pretext:
“When the socialists realized that the workers were not getting poorer under capitalism, but richer, they changed their strategy. Today, the class struggle between capitalists and workers has been replaced by alleged conflicts between men and women or between man and nature. It is claimed that to save the environment, population growth must be controlled; abortion is promoted”.
4. Public opinion is the result of decades of “brainwashing” in the direction desired by the elites:
“The neo-Marxists have changed public opinion in a long process of taking control of the media, the universities and even international organizations. As everyone here knows, the WEF is one of the latter. Socialist ideas must be fought frontally and vociferously.”
5. Socialists have more than one name:
“There are many varieties of socialism in the broadest sense. Socialists are not only those who call themselves socialists, but also social democrats, Christian democrats, communists, Keynesians, Nazis, nationalists and globalists. They all share a belief in regulation and the state”.
6. The real heroes are the entrepreneurs. The state, on the other hand, is only a threat to freedom:
“The real heroes of society are entrepreneurs. They are creators of wealth who can be proud of making profits by meeting the needs of others. They should not be allied with the state, not even through the WEF. The state is not the solution. The state is the problem. The state is a threat to freedom.”
Since Milei’s speech, the number of views of his video on the official WEF channel has exceeded half a million. Is that a lot? Just look at the other “great speakers” who have lagged far behind. The conversation with US Secretary of State Antony Blinken, for example, reached 56,000, the speech by EU Commission President Ursula von der Leyen 42,000, and the other speeches received even less attention. (As at the end of January 2024)
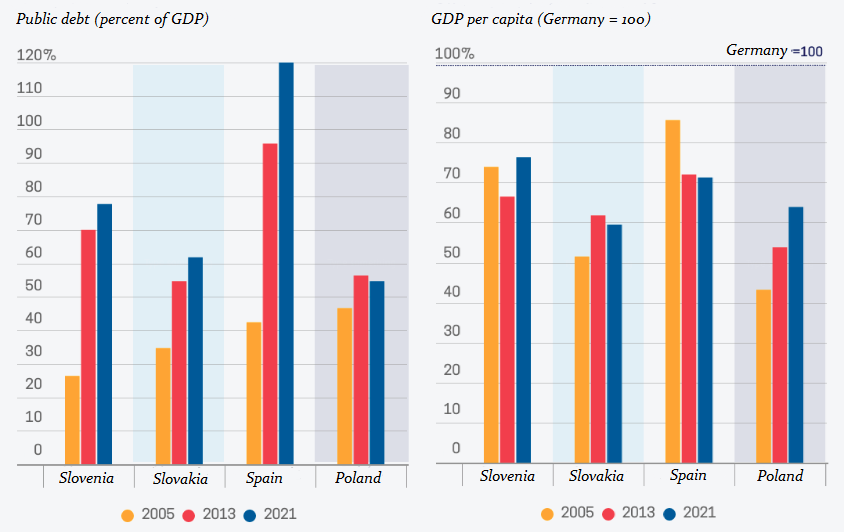
An interesting case is the speech by Spanish Prime Minister Pedro Sanchez, who, as the country’s extreme socialist leader – i.e. in complete opposition to Milei – made a staid appearance and barely reached 12,000 views. In his speech, he talks about everything and nothing. He mentions the current problems and challenges, but offers no solutions. The Spanish Prime Minister’s speech was preceded by congratulations on Spain’s strong economic growth, which the Prime Minister himself also boasted about. So let us quote here the conclusions of one of Spain’s leading independent economists, Daniel Lacalle, who summarizes it as follows: ‘The reality in which Spain finds itself today is different from the one presented by the Spanish government under Pedro Sanchez. The ruling socialists are using the same techniques that the Greek socialists resorted to at the end of the 1990s. Namely, they are increasing public spending and debt to hide the fact that investment and consumption in the country have stalled and exports are falling. Taxes are being increased because/although tax revenues have been falling in recent years. The choice between because and although in the last sentence reveals what you think about the right economic policy.