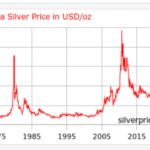
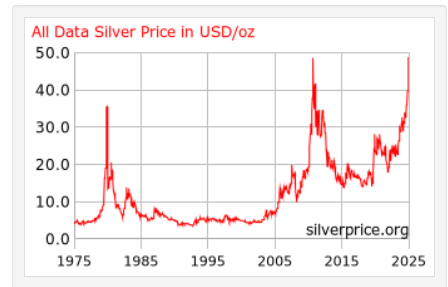
The price of silver has performed very well since the beginning of the year, due to both investment and industrial demand (mainly due to the production of solar panels by China), but it was only recently that information emerged about a real decline in supply in this market. As a result, the silver price hit new all-time records.
The supply crisis was to begin with India and the Diwali festival there. At this time, Indians bought millions of rupees worth of jewelry to worship their goddess of wealth, Lakshmi. In previous years, this demand was for gold and the supply came from Asian refineries. This year, however, was different. For months, there has been speculation on social media in India that after such a big rally in gold, it is now time for silver. The breakthrough was to be the statement by banker and investor Sartak Ahuja, who in one of the videos targeting his 3 million follower community, stated that the silver to gold price ratio, currently 100:1 makes silver the obvious choice this year. After the video with the statements was released, Indians started buying silver massively, leading to the first silver shortage at the largest precious metals refinery in India. As per various Indian sources, the demand for silver was huge, never seen before, leading to a situation where Indians had to pay 8 dollars more for an ounce of silver than in the world markets.
Due to the fact that the Chinese refineries were not working at the time because of a week’s break (public holidays), demand from Indian refineries shifted to the West and in particular to the LBMA (Bullion Stock Exchange in London) in London. There it quickly became apparent that 83% of the accumulated silver in LBMA warehouses is in the hands of ETFs and cannot be lent out (the refinery borrows the silver, processes it and sells it, earns a margin on it and then buys it back and returns it to their lender). Considering that there are 790 million ounces of silver in the LBMA, only 150 million ounces can be made available to refineries and other institutions. Thus, the low availability of metal led to an increase in silver rental costs to 39% per year if the rental period of the metal is 1 month.
As Metal Focus reports, the cost of borrowing silver for one day (overnight) rose to 200%, and the difference between the buy and sell price (spread) rose so high that trading became impossible. Although there are currently already forecasts for higher silver prices in 2026 (Bank of America is betting on $65 per ounce in 2026, which seems very likely), the current crisis is expected to subside within a few days when the LBMA finally delivers silver from New York and China.