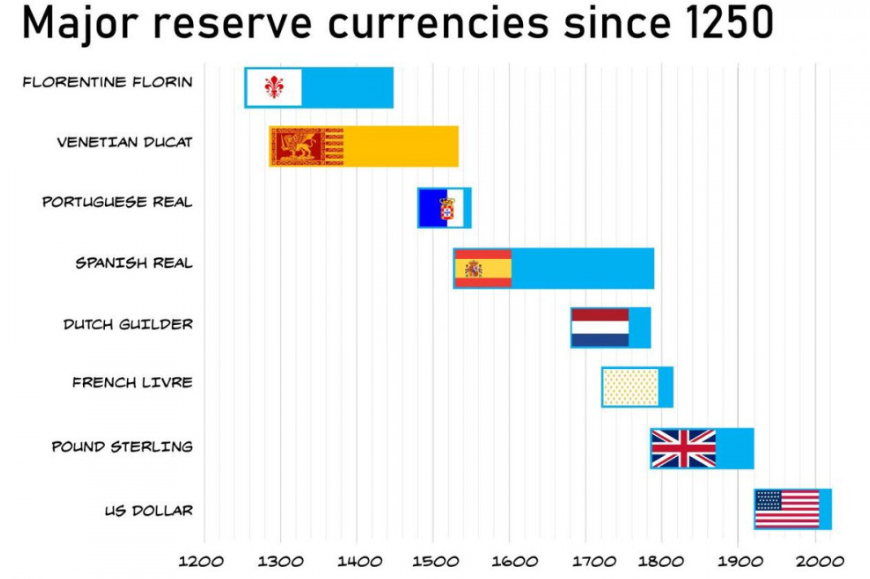
The Balkans, similarly to the Iberian Peninsula, have been the place where Muslims have made inroads into the European continent; the region has often been a scenery for many hostilities between both the local small powers and the external large players. In the 20 century alone the region saw two wars of 1912-1913, two world wars (with the first being triggered here) and numerous civil armed conflicts among the republics of former Yugoslavia.
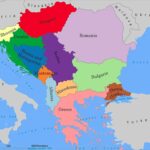
Broadly, the Balkans can be divided into Eastern (Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, a small chunk of Turkey this side the Bosporus), Western (territories occupied once by Yugoslavia) and Southern (Greece).
Ethnically, the Balkans is home to Slavic (Slovenians, Croats, Serbs, Montenegrins, Bosnians, Macedonians, Bulgarians) and non-Slavic peoples (Hungarians, Romanians, Albanians, Greeks and Turks). In terms of religion (the fact that determines to which civilisation model a particular nation belongs), the inhabitants are either Muslim (most of Albanians, some Bosnians, Turks) or Christian of either the Catholic (Slovenians, Croats, Hungarians, a sizable part of Albanians, especially in the north of the country) and Orthodox (Romanians, Bulgarians, Serbs, Bosnians, Montenegrins, Macedonians, Greeks) creeds. Notice in passing that not all Slavs are Orthodox Christian (some are Catholic, some are Muslim) and that Orthodox Christianity is the creed of non-Slavic Greeks and Romanians.
The three great historical influences were two European and one Asian powers. The former were the Germans either of the Hapsburg and then Austria-Hungary monarchy, followed by Germany, and Russia; the latter was the Ottoman Empire or its descendant: Turkey. It was in the Middle Ages that Hungary began to rule Croatia and north-western parts of today’s Romania. The German Habsburgs dynasty gradually expanded to control Hungary with the latter’s territorial gains as well as making military or diplomatic conquests of its own, extending its rule by incorporating Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1908. It was the German house of Hohenzollern, which provided monarchs to the nascent forms of statehood of Greece, Bulgaria and Romania. The Russian Empire rendered significant aid to Greece and then to Serbia and Bulgaria in the respective nations’ wars of independence from the Ottoman Empire. Turkey may have withdrawn from the region, but it maintained close ties to the German Empire and the Third Reich and left behind a numerically significant Muslim population. Soviet Russia continued to be interested in the Balkans and gained control over most of it after the Second World War. Continue reading