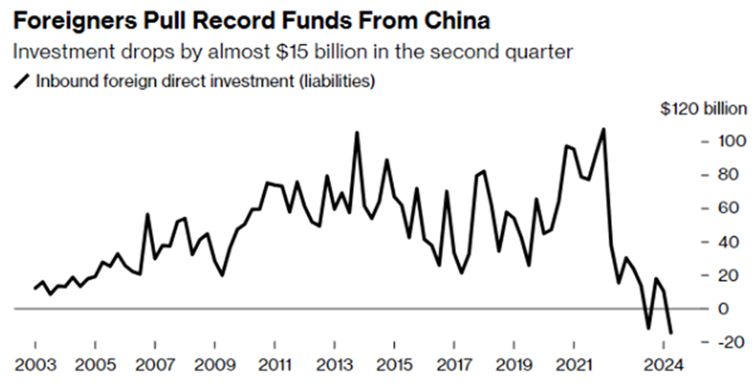
Original published Aug 7, 2017
This affair is a huge scandal. It involves the current president of the European Council, Donald Tusk, and his son Michał. Donald Tusk presents himself as a politician who cares very much about the rule of law in Poland. When he was Poland’s prime minister, however, he ignored information given to him by the Chief of the Internal Security Agency and the President of the National Bank of Poland. They both warned him that his son was involved in a Ponzi scheme called Amber Gold.
The case is being investigated by the Polish government, which set up a special Inquiry Committee. Of course, Donald Tusk is denying all the accusations, but at the same time he is criticizing Warsaw for failing to enforce democracy and the rule of law. The question is whether Donald Tusk is not acting in self-defence and aiming at toppling the government, which set up the Inquiry Committee on the Amber Gold.
Poland’s former prime minister and currently the president of the European Council is still the spiritual leader of the political opposition in his own country and is doing his best to earn much respect in Brussels. People in Poland think he is Angela Merkel’s man, which is why he was promoted so high in the EU structures. The average Western European probably believes that Donald Tusk has been given this high-ranking post as a reward for his contribution to establishing the rule of law in Poland. The average Western European probably does not know that Donald Tusk’s Civic Platform party experienced a resounding defeat in the parliamentary election just a few months after his transfer to Brussels. The Polish people say that the promotion of the Polish prime minister may have been a helping hand extended to him by Angela Merkel, who thus paid him for his obedience and saved him from the verdict of the voters and, (who knows?) the verdict of the court of law (see below).
Currently, Donald Tusk seems to be taking steps against his own country in retaliation for the fact that the new government has set up a committee to investigate his and his son’s participation in the largest fraud of the recent years. Contrarily to his pledge of impartiality and neutrality towards all 28 member states,” Donald Tusk seizes every opportunity to attack and rebuke Poland. In 2016/2017, when for almost two months the Polish parliament was occupied by the opposition, Tusk threatened Poland with legal consequences for the 2017 budget that had been passed allegedly in violation of the regulations. Poland’s former prime minister put a pressure on the Polish authorities exactly at the time when the government’s opponents held protests in Warsaw, which means that Donald Tusk for all practical purposes was supporting an attempted coup d’etat and did his best to create bad press in the West for his own country. Continue reading →